Mass manufacture of carbon fibre parts
The world energy crisis has become more severe since the beginning of the 21st century. The reduction of fuel consumption and emissions are some of the automotive industry's main problems that need to be solved. More than half of the total volume in the production of a modern car consists of cast iron and steel parts, about 11 % – plastics, aluminum alloys (9 %); rubber 7% and 3% respectively. The share of non-ferrous alloys (magnesium, titanium, copper, and zinc) is about 1%; other materials (varnishes, paints, electric wires, facing materials, etc.) make 13.5 % as shown
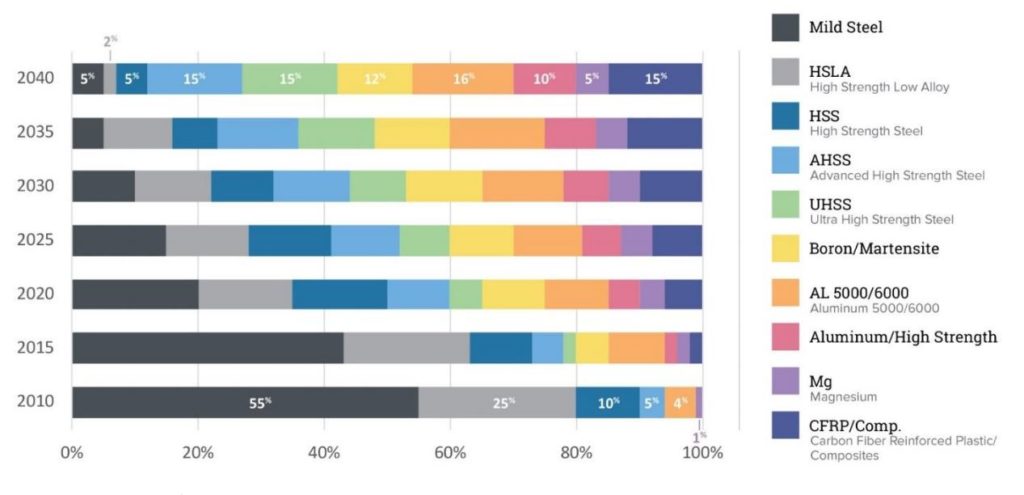
To overcome the problem of energy efficiency, various researchers suggested that different parts of the vehicle could be replaced with different lightweight materials such as alloys and other traditional materials to reduce the weight of cars

Every 10 kg of reduction of a vehicle reduces fuel consumption and leads to a drop in carbon emission of 1g/km. Carbon fibre compounds have low weight, high strength, high rigidity, good vibration resistance, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and many other advantages.

Carbon fiber is mostly used in space, racing, planes, and supercars because it higher cost. In recent years BMW used it for "cheaper" cars for example the BMW i3 had a carbon fiber plastic chassis.

Bmws chassis were made with resin transfer molding.
Which is a process in which resin is introduced to a laminate containing dry fiber. The fiber is typically applied to a mandrel through filament winding, or by a hand layup process with woven fabrics including glass, carbon, and aramid. There are many forms of RTM, but in general, a resin is pulled or pushed into the fiber laminate through the use of vacuum and/or pressure. RTM resins are typically low in viscosity to better facilitate fiber wet out. In processes, such as filament winding, where the fiber is tensioned during application to a mandrel, resin viscosity during RTM is a critical design factor. To keep processing times to a minimum, RTM molds are heated to accelerate resin cure time and solidification. Once cured, the mold cavity is opened and part is removed by an operator for the mandrel extraction process.
Carbon fiber reinforced parts are light, strong, and load-bearing, structural parts. Cutting weight from cars is important, as automakers push to hit electrification. Less weight equals more range. The problem boils down to high cost and slow processing times.
Carbon fiber for automotive costs $10 to $12 a pound, compared to less than a buck for steel. That's more than half the $35 price a decade ago, but to see more widespread adoption, it needs to get down to about $5 or $6 a pound, they said. According to JEC Americas. That's still too high for mass adoption.